Out of plane elastic compressive properties of metallic honeycomb structures
By Frédéric Brun
JEC COMPOSITES MAGAZINE_N° 106 July 2016
application/pdf – 0.96 MB
DownloadThis study explores the mechanical performance of a new metallic honeycomb structure, developed to overcome the limitations of traditional hexagonal structures. While the hexagonal configuration is widely used in industry, it exhibits marked mechanical anisotropy, particularly in shear, favoring one direction over another, and suffers from parasitic deformations under complex loading.
To address these weaknesses, a novel corrugated cell topology was designed. This specific geometry reduces anisotropy in mechanical properties, increases formability (the ability to conform to complex shapes without parasitic deformation), and improves adhesion to the skins of sandwich structures. It remains compatible with existing industrial manufacturing processes, which is an advantage for its widespread adoption.
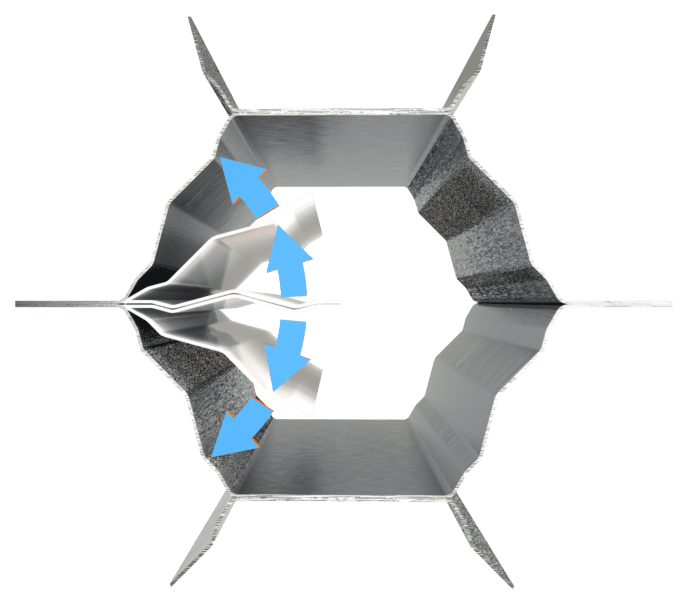
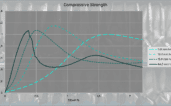
Comparative mechanical tests were performed in compression, crushing, and shear according to current standards. To ensure a fair comparison, conventional hexagonal structures and the modified structures were tested with similar densities. The results showed that the new structure offers overall superior mechanical performance compared to conventional hexagonal structures, even at higher densities. In particular, it exhibits better resistance to crushing and compression and maintains very good shear strength, despite slight reductions in stiffness in certain directions.
Another significant advantage observed is improved energy absorption capacity under dynamic stresses, which is crucial for protective and lightweight structural applications. Furthermore, the new geometry facilitates adhesive application and enhances adhesion between the core and skins, allowing for a reduction in the amount of adhesive required.
In conclusion, this study highlights that a simple modification of cell geometry can lead to significant gains in mechanical performance, while also optimizing other practical aspects such as formability and assembly. This opens up exciting possibilities for developing lighter, stronger, and more economical structures in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and space.
JEC COMPOSITES MAGAZINE_N° 106 July 2016
application/pdf – 0.96 MB
Download